More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

cdixon
1 year ago
2000s Toys, Secrets, and Cycles
During the dot-com bust, I started my internet career. People used the internet intermittently to check email, plan travel, and do research. The average internet user spent 30 minutes online a day, compared to 7 today. To use the internet, you had to "log on" (most people still used dial-up), unlike today's always-on, high-speed mobile internet. In 2001, Amazon's market cap was $2.2B, 1/500th of what it is today. A study asked Americans if they'd adopt broadband, and most said no. They didn't see a need to speed up email, the most popular internet use. The National Academy of Sciences ranked the internet 13th among the 100 greatest inventions, below radio and phones. The internet was a cool invention, but it had limited uses and wasn't a good place to build a business.
A small but growing movement of developers and founders believed the internet could be more than a read-only medium, allowing anyone to create and publish. This is web 2. The runner up name was read-write web. (These terms were used in prominent publications and conferences.)
Web 2 concepts included letting users publish whatever they want ("user generated content" was a buzzword), social graphs, APIs and mashups (what we call composability today), and tagging over hierarchical navigation. Technical innovations occurred. A seemingly simple but important one was dynamically updating web pages without reloading. This is now how people expect web apps to work. Mobile devices that could access the web were niche (I was an avid Sidekick user).
The contrast between what smart founders and engineers discussed over dinner and on weekends and what the mainstream tech world took seriously during the week was striking. Enterprise security appliances, essentially preloaded servers with security software, were a popular trend. Many of the same people would talk about "serious" products at work, then talk about consumer internet products and web 2. It was tech's biggest news. Web 2 products were seen as toys, not real businesses. They were hobbies, not work-related.
There's a strong correlation between rich product design spaces and what smart people find interesting, which took me some time to learn and led to blog posts like "The next big thing will start out looking like a toy" Web 2's novel product design possibilities sparked dinner and weekend conversations. Imagine combining these features. What if you used this pattern elsewhere? What new product ideas are next? This excited people. "Serious stuff" like security appliances seemed more limited.
The small and passionate web 2 community also stood out. I attended the first New York Tech meetup in 2004. Everyone fit in Meetup's small conference room. Late at night, people demoed their software and chatted. I have old friends. Sometimes I get asked how I first met old friends like Fred Wilson and Alexis Ohanian. These topics didn't interest many people, especially on the east coast. We were friends. Real community. Alex Rampell, who now works with me at a16z, is someone I met in 2003 when a friend said, "Hey, I met someone else interested in consumer internet." Rare. People were focused and enthusiastic. Revolution seemed imminent. We knew a secret nobody else did.
My web 2 startup was called SiteAdvisor. When my co-founders and I started developing the idea in 2003, web security was out of control. Phishing and spyware were common on Internet Explorer PCs. SiteAdvisor was designed to warn users about security threats like phishing and spyware, and then, using web 2 concepts like user-generated reviews, add more subjective judgments (similar to what TrustPilot seems to do today). This staged approach was common at the time; I called it "Come for the tool, stay for the network." We built APIs, encouraged mashups, and did SEO marketing.
Yahoo's 2005 acquisitions of Flickr and Delicious boosted web 2 in 2005. By today's standards, the amounts were small, around $30M each, but it was a signal. Web 2 was assumed to be a fun hobby, a way to build cool stuff, but not a business. Yahoo was a savvy company that said it would make web 2 a priority.
As I recall, that's when web 2 started becoming mainstream tech. Early web 2 founders transitioned successfully. Other entrepreneurs built on the early enthusiasts' work. Competition shifted from ideation to execution. You had to decide if you wanted to be an idealistic indie bar band or a pragmatic stadium band.
Web 2 was booming in 2007 Facebook passed 10M users, Twitter grew and got VC funding, and Google bought YouTube. The 2008 financial crisis tested entrepreneurs' resolve. Smart people predicted another great depression as tech funding dried up.
Many people struggled during the recession. 2008-2011 was a golden age for startups. By 2009, talented founders were flooding Apple's iPhone app store. Mobile apps were booming. Uber, Venmo, Snap, and Instagram were all founded between 2009 and 2011. Social media (which had replaced web 2), cloud computing (which enabled apps to scale server side), and smartphones converged. Even if social, cloud, and mobile improve linearly, the combination could improve exponentially.
This chart shows how I view product and financial cycles. Product and financial cycles evolve separately. The Nasdaq index is a proxy for the financial sentiment. Financial sentiment wildly fluctuates.
Next row shows iconic startup or product years. Bottom-row product cycles dictate timing. Product cycles are more predictable than financial cycles because they follow internal logic. In the incubation phase, enthusiasts build products for other enthusiasts on nights and weekends. When the right mix of technology, talent, and community knowledge arrives, products go mainstream. (I show the biggest tech cycles in the chart, but smaller ones happen, like web 2 in the 2000s and fintech and SaaS in the 2010s.)
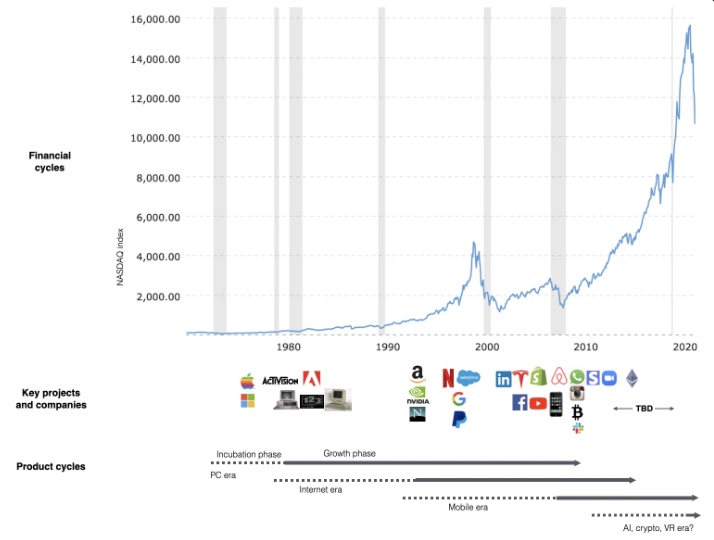
Tech has changed since the 2000s. Few tech giants dominate the internet, exerting economic and cultural influence. In the 2000s, web 2 was ignored or dismissed as trivial. Entrenched interests respond aggressively to new movements that could threaten them. Creative patterns from the 2000s continue today, driven by enthusiasts who see possibilities where others don't. Know where to look. Crypto and web 3 are where I'd start.
Today's negative financial sentiment reminds me of 2008. If we face a prolonged downturn, we can learn from 2008 by preserving capital and focusing on the long term. Keep an eye on the product cycle. Smart people are interested in things with product potential. This becomes true. Toys become necessities. Hobbies become mainstream. Optimists build the future, not cynics.
Full article is available here

Caleb Naysmith
1 year ago
Ads Coming to Medium?
Could this happen?
Medium isn't like other social media giants. It wasn't a dot-com startup that became a multi-trillion-dollar social media firm. It launched in 2012 but didn't gain popularity until later. Now, it's one of the largest sites by web traffic, but it's still little compared to most. Most of Medium's traffic is external, but they don't run advertisements, so it's all about memberships.
Medium isn't profitable, but they don't disclose how terrible the problem is. Most of the $163 million they raised has been spent or used for acquisitions. If the money turns off, Medium can't stop paying its writers since the site dies. Writers must be paid, but they can't substantially slash payment without hurting the platform. The existing model needs scale to be viable and has a low ceiling. Facebook and other free social media platforms are struggling to retain users. Here, you must pay to appreciate it, and it's bad for writers AND readers. If I had the same Medium stats on YouTube, I'd make thousands of dollars a month.
Then what? Medium has tried to monetize by offering writers a cut of new members, but that's unsustainable. People-based growth is limited. Imagine recruiting non-Facebook users and getting them to pay to join. Some may, but I'd rather write.
Alternatives:
Donation buttons
Tiered subscriptions ($5, $10, $25, etc.)
Expanding content
and these may be short-term fixes, but they're not as profitable as allowing ads. Advertisements can pay several dollars per click and cents every view. If you get 40,000 views a month like me, that's several thousand instead of a few hundred. Also, Medium would have enough money to split ad revenue with writers, who would make more. I'm among the top 6% of Medium writers. Only 6% of Medium writers make more than $100, and I made $500 with 35,000 views last month. Compared to YouTube, the top 1% of Medium authors make a lot. Mr. Beast and PewDiePie make MILLIONS a month, yet top Medium writers make tens of thousands. Sure, paying 3 or 4 people a few grand, or perhaps tens of thousands, will keep them around. What if great authors leveraged their following to go huge on YouTube and abandoned Medium? If people use Medium to get successful on other platforms, Medium will be continuously cycling through authors and paying them to stay.
Ads might make writing on Medium more profitable than making videos on YouTube because they could preserve the present freemium model and pay users based on internal views. The $5 might be ad-free.
Consider: Would you accept Medium ads? A $5 ad-free version + pay-as-you-go, etc. What are your thoughts on this?
Original post available here

Dani Herrera
1 year ago
What prevents companies from disclosing salary information?

Yes, salary details ought to be mentioned in job postings. Recruiters and candidates both agree, so why doesn't it happen?
The short answer is “Unfortunately, it’s not the Recruiter’s decision”. The longer answer is well… A LOT.
Starting in November 2022, NYC employers must include salary ranges in job postings. It should have started in May, but companies balked.
I'm thrilled about salary transparency. This decision will promote fair, inclusive, and equitable hiring practices, and I'm sure other states will follow suit. Good news!
Candidates, recruiters, and ED&I practitioners have advocated for pay transparency for years. Why the opposition?
Let's quickly review why companies have trouble sharing salary bands.
💰 Pay Parity
Many companies and leaders still oppose pay parity. Yes, even in 2022.
💰 Pay Equity
Many companies believe in pay parity and have reviewed their internal processes and systems to ensure equality.
However, Pay Equity affects who gets roles/promotions/salary raises/bonuses and when. Enter the pay gap!
💰Pay Transparency and its impact on Talent Retention
Sharing salary bands with external candidates (and the world) means current employees will have access to that information, which is one of the main reasons companies don't share salary data.
If a company has Pay Parity and Pay Equity issues, they probably have a Pay Transparency policy as well.
Sharing salary information with external candidates without ensuring current employees understand their own salary bands and how promotions/raises are decided could impact talent retention strategies.
This information should help clarify recent conversations.
You might also like

Alex Mathers
1 year ago
8 guidelines to help you achieve your objectives 5x fast

If you waste time every day, even though you're ambitious, you're not alone.
Many of us could use some new time-management strategies, like these:
Focus on the following three.
You're thinking about everything at once.
You're overpowered.
It's mental. We just have what's in front of us. So savor the moment's beauty.
Prioritize 1-3 things.
To be one of the most productive people you and I know, follow these steps.
Get along with boredom.
Many of us grow bored, sweat, and turn on Netflix.
We shout, "I'm rarely bored!" Look at me! I'm happy.
Shut it, Sally.
You're not making wonderful things for the world. Boredom matters.
If you can sit with it for a second, you'll get insight. Boredom? Breathe.
Go blank.
Then watch your creativity grow.
Check your MacroVision once more.
We don't know what to do with our time, which contributes to time-wasting.
Nobody does, either. Jeff Bezos won't hand-deliver that crap to you.
Daily vision checks are required.
Also:
What are 5 things you'd love to create in the next 5 years?
You're soul-searching. It's food.
Return here regularly, and you'll adore the high you get from doing valuable work.
Improve your thinking.
What's Alex's latest nonsense?
I'm talking about overcoming our own thoughts. Worrying wastes so much time.
Too many of us are assaulted by lies, myths, and insecurity.
Stop letting your worries massage you into a worried coma like a Thai woman.
Optimizing your thoughts requires accepting what you can't control.
It means letting go of unhelpful thoughts and returning to the moment.
Keep your blood sugar level.
I gave up gluten, donuts, and sweets.
This has really boosted my energy.
Blood-sugar-spiking carbs make us irritable and tired.
These day-to-day ups and downs aren't productive. It's crucial.
Know how your diet affects insulin levels. Now I have more energy and can do more without clenching my teeth.
Reduce harmful carbs to boost energy.
Create a focused setting for yourself.
When we optimize the mind, we have more energy and use our time better because we're not tense.
Changing our environment can also help us focus. Disabling alerts is one example.
Too hot makes me procrastinate and irritable.
List five items that hinder your productivity.
You may be amazed at how much you may improve by removing distractions.
Be responsible.
Accountability is a time-saver.
Creating an emotional pull to finish things.
Writing down our goals makes us accountable.
We can engage a coach or work with an accountability partner to feel horrible if we don't show up and finish on time.
‘Hey Jake, I’m going to write 1000 words every day for 30 days — you need to make sure I do.’ ‘Sure thing, Nathan, I’ll be making sure you check in daily with me.’
Tick.
You might also blog about your ambitions to show your dedication.
Now you can't hide when you promised to appear.
Acquire a liking for bravery.
Boldness changes everything.
I sometimes feel lazy and wonder why. If my food and sleep are in order, I should assess my footing.
Most of us live backward. Doubtful. Uncertain. Feelings govern us.
Backfooting isn't living. It's lame, and you'll soon melt. Live boldly now.
Be assertive.
Get disgustingly into everything. Expand.
Even if it's hard, stop being a b*tch.
Those that make Mr. Bold Bear their spirit animal benefit. Save time to maximize your effect.

The woman
1 year ago
The best lesson from Sundar Pichai is that success and stress don't mix.
His regular regimen teaches stress management.

In 1995, an Indian graduate visited the US. He obtained a scholarship to Stanford after graduating from IIT with a silver medal. First flight. His ticket cost a year's income. His head was full.
Pichai Sundararajan is his full name. He became Google's CEO and a world leader. Mr. Pichai transformed technology and inspired millions to dream big.
This article reveals his daily schedule.
Mornings
While many of us dread Mondays, Mr. Pichai uses the day to contemplate.
A typical Indian morning. He awakens between 6:30 and 7 a.m. He avoids working out in the mornings.
Mr. Pichai oversees the internet, but he reads a real newspaper every morning.
Pichai mentioned that he usually enjoys a quiet breakfast during which he reads the news to get a good sense of what’s happening in the world. Pichai often has an omelet for breakfast and reads while doing so. The native of Chennai, India, continues to enjoy his daily cup of tea, which he describes as being “very English.”
Pichai starts his day. BuzzFeed's Mat Honan called the CEO Banana Republic dad.
Overthinking in the morning is a bad idea. It's crucial to clear our brains and give ourselves time in the morning before we hit traffic.
Mr. Pichai's morning ritual shows how to stay calm. Wharton Business School found that those who start the day calmly tend to stay that way. It's worth doing regularly.
And he didn't forget his roots.
Afternoons
He has a busy work schedule, as you can imagine. Running one of the world's largest firm takes time, energy, and effort. He prioritizes his work. Monitoring corporate performance and guaranteeing worker efficiency.
Sundar Pichai spends 7-8 hours a day to improve Google. He's noted for changing the company's culture. He wants to boost employee job satisfaction and performance.
His work won him recognition within the company.
Pichai received a 96% approval rating from Glassdoor users in 2017.
Mr. Pichai stresses work satisfaction. Each day is a new canvas for him to find ways to enrich people's job and personal lives.
His work offers countless lessons. According to several profiles and press sources, the Google CEO is a savvy negotiator. Mr. Pichai's success came from his strong personality, work ethic, discipline, simplicity, and hard labor.
Evenings
His evenings are spent with family after a busy day. Sundar Pichai's professional and personal lives are balanced. Sundar Pichai is a night owl who re-energizes about 9 p.m.
However, he claims to be most productive after 10 p.m., and he thinks doing a lot of work at that time is really useful. But he ensures he sleeps for around 7–8 hours every day. He enjoys long walks with his dog and enjoys watching NSDR on YouTube. It helps him in relaxing and sleep better.
His regular routine teaches us what? Work wisely, not hard, discipline, vision, etc. His stress management is key. Leading one of the world's largest firm with 85,000 employees is scary.
The pressure to achieve may ruin a day. Overworked employees are more likely to make mistakes or be angry with coworkers, according to the Family Work Institute. They can't handle daily problems, making the house more stressful than the office.
Walking your dog, having fun with friends, and having hobbies are as vital as your office.

Faisal Khan
1 year ago
4 typical methods of crypto market manipulation

Market fraud
Due to its decentralized and fragmented character, the crypto market has integrity difficulties.
Cryptocurrencies are an immature sector, therefore market manipulation becomes a bigger issue. Many research have attempted to uncover these abuses. CryptoCompare's newest one highlights some of the industry's most typical scams.
Why are these concerns so common in the crypto market? First, even the largest centralized exchanges remain unregulated due to industry immaturity. A low-liquidity market segment makes an attack more harmful. Finally, market surveillance solutions not implemented reduce transparency.
In CryptoCompare's latest exchange benchmark, 62.4% of assessed exchanges had a market surveillance system, although only 18.1% utilised an external solution. To address market integrity, this measure must improve dramatically. Before discussing the report's malpractices, note that this is not a full list of attacks and hacks.
Clean Trading
An investor buys and sells concurrently to increase the asset's price. Centralized and decentralized exchanges show this misconduct. 23 exchanges have a volume-volatility correlation < 0.1 during the previous 100 days, according to CryptoCompares. In August 2022, Exchange A reported $2.5 trillion in artificial and/or erroneous volume, up from $33.8 billion the month before.

Spoofing
Criminals create and cancel fake orders before they can be filled. Since manipulators can hide in larger trading volumes, larger exchanges have more spoofing. A trader placed a 20.8 BTC ask order at $19,036 when BTC was trading at $19,043. BTC declined 0.13% to $19,018 in a minute. At 18:48, the trader canceled the ask order without filling it.

Front-Running
Most cryptocurrency front-running involves inside trading. Traditional stock markets forbid this. Since most digital asset information is public, this is harder. Retailers could utilize bots to front-run.
CryptoCompare found digital wallets of people who traded like insiders on exchange listings. The figure below shows excess cumulative anomalous returns (CAR) before a coin listing on an exchange.

Finally, LAYERING is a sequence of spoofs in which successive orders are put along a ladder of greater (layering offers) or lower (layering bids) values. The paper concludes with recommendations to mitigate market manipulation. Exchange data transparency, market surveillance, and regulatory oversight could reduce manipulative tactics.
